命令简介
tree 是一个实用的 Linux 目录列表工具,以树形结构递归显示文件和目录,直观展示层级关系。它支持自定义过滤、排序、输出格式等功能,是管理文件系统的利器。
安装tree
大多数 Linux 系统默认未安装 tree,需手动安装:
#Debian/Ubuntu
sudo apt install tree
#debian:https://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/pool/main/t/tree/
#Ubuntu:https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/pool/universe/t/tree
#RedHat/CentOS
sudo yum install tree
#可以使用wget命令根据rpm地址下载后安装
#rhel7/centos7:https://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos-vault/7.9.2009/os/x86_64/Packages/tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64.rpm
#rhel8/centos8:https://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos-vault/8.5.2111/BaseOS/x86_64/os/Packages/tree-1.7.0-15.el8.x86_64.rpm
#rhel9/centos stream9:https://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos-stream/9-stream/BaseOS/x86_64/os/Packages/tree-1.8.0-10.el9.x86_64.rpm
#Arch/Manjaro
sudo pacman -S tree
#Manjaro:https://mirrors.aliyun.com/manjaro/pool/sync/tree-2.2.1-1-x86_64.pkg.tar.zst
#Arch:https://mirrors.aliyun.com/archlinux/pool/packages/tree-2.2.1-1-x86_64.pkg.tar.zst用法
tree命令的语法格式如下
tree [选项] [目标目录]
#选项可选
#目标目录可选tree命令的常用选项及说明如下
------- 列表选项 -------
-a #显示所有文件和目录
-d #显示目录名称而非文件
-l #如遇到性质为符号连接的目录,直接列出该连接所指向的原始目录
-f #在每个文件或目录之前,显示完整的相对路径名称
-x #将范围局限在现行的文件系统中,若指定目录下的某些子目录,其存放于另一个文件系统上,则将该目录予以排除在寻找范围外
-L level #限制目录显示层级
-R #不要列出与给定模式匹配的文件
-P pattern #<范本样式> 只显示符合范本样式的文件和目录名称
-I pattern #不列出与给定模式匹配的文件
--ignore-case #模式匹配时忽略大小写
--matchdirs #在-P模式匹配中包含目录名
--noreport #关闭树列表末尾的文件/目录计数
--charset X #将字符集X用于终端/HTML和缩进行输出
--filelimit #请勿下载包含超过个文件的目录
--timefmt <f> #根据格式<f>打印和格式化时间
-o filename #输出到文件而不是输出到屏幕
--du #打印目录大小
--prune #从输出中删除空目录
-------- 文件选项 ---------
-q #用“?”号取代控制字符,列出文件和目录名称
-N #直接列出文件和目录名称,包括控制字符
-Q #用双引号引用文件名
-p #列出权限标示
-u #列出文件或目录的拥有者名称,没有对应的名称时,则显示用户识别码
-g #列出文件或目录的所属群组名称,没有对应的名称时,则显示群组识别码
-s #列出文件和目录大小
-h #以更易读的方式打印大小
--si #类似于-h,但使用国际单位制(1000的幂)
-D #列出文件或目录的更改时间
-F #在执行文件,目录,Socket,符号连接,管道名称名称,各自加上"*","/","@","|"号
--inodes #打印每个文件的索引节点号
--device #打印每个文件所属的设备ID号
------- 排序选项 -------
-v #按字母数字对文件进行排序
-t #用文件和目录的更改时间排序
-c #按最后的更改时间对文件进行排序
-U #天下黄河
-r #反转排序顺序
--dirsfirst #在文件之前列出目录(-U禁用)
--sort X #选择排序:名称、版本、大小、时间、时间
------- 图形选项 ------
-i #不以阶梯状列出文件和目录名称
-A #使用ASNI绘图字符显示树状图而非以ASCII字符组合
-S #使用CP437(控制台)图形压痕线打印
-n #始终关闭着色(-C覆盖)
-C #在文件和目录清单加上色彩,便于区分各种类型
------- XML / HTML / JSON选项 -------
-X #打印出XML表示形式的树
-J #打印出JSON表示形式的树
-H baseHREF #打印出以baseHREF为顶部目录的HTML格式
-T string #将默认HTML标题和H1标头替换为字符串
--nolinks #关闭HTML输出中的超链接
---- 杂项选项 ----
--version #输入版本信息
--help #打印使用帮助信息
-- #选项处理终止符命令案例场景
1.基础用法
显示当前目录的树状结构
[root@blog ~]# tree
.
├── anaconda-ks.cfg
├── dir1
│ ├── file1.txt
│ └── subdir
└── dir2
└── report.pdf
3 directories, 2 files显示指定目录的结构
[root@blog ~]# tree /var/log/
/var/log/
├── anaconda
│ ├── anaconda.log
│ ├── dbus.log
│ ├── lvm.log
│ ├── packaging.log
│ ├── program.log
├── audit
│ └── audit.log
├── boot.log
├── btmp
├── chrony
├── vmware-vmusr-root.log
└── wtmp
3 directories, 10 files2.核心参数应用场景
层级控制(-L)
[root@blog ~]# tree -L 1 #仅显示1级目录
.
├── anaconda-ks.cfg
├── dir1
└── dir2
2 directories, 1 files隐藏文件显示(-a)
[root@blog ~]# tree -a #显示以.开头的隐藏文件
.
├── anaconda-ks.cfg
├── .bash_history
├── .bash_logout
├── .bash_profile
├── .bashrc
├── .cache
├── .config
├── .cshrc
├── dir1
│ ├── file1.txt
│ └── subdir
├── dir2
│ └── report.pdf
├── .local
│ ├── share
│ └── state
├── .ssh
├── .tcshrc
└── .Xauthority
9 directories, 9 files仅显示目录及子目录(-d)
[root@blog ~]# tree -d
.
├── dir1
│ └── subdir
└── dir2
3 directories显示文件权限、所有者和所有组(-p、-u、-g)
[root@blog ~]# tree -p -u -g #或使用tree -pug
.
├── [-rw------- root root ] anaconda-ks.cfg
├── [drwxr-xr-x root root ] dir1
│ ├── [-rw-r--r-- root root ] file1.txt
│ └── [drwxr-xr-x root root ] subdir
└── [drwxr-xr-x root root ] dir2
└── [-rw-r--r-- root root ] report.pdf
3 directories, 2 files完整路径显示(-f)
[root@blog ~]# tree -f
/root
├── /root/anaconda-ks.cfg
├── /root/dir1
│ ├── /root/dir1/file1.txt
│ └── /root/dir1/subdir
└── /root/dir2
└── /root/dir2/report.pdf
3 directories, 3 files
#以上案例全部是在/root目录下操作,没有写目录名,则用.代表当前文件夹排除过滤(-I)
[root@blog ~]# tree -I "subdir|*.pdf" #排除subdir和.pdf文件
.
├── anaconda-ks.cfg
├── dir1
│ └── file1.txt
└── dir2
2 directories, 2 files输出重定向(-o)
[root@blog ~]# tree -o structure.txt #将结果保存到文件
#验证
[root@blog ~]# cat structure.txt
.
├── anaconda-ks.cfg
├── dir1
│ ├── file1.txt
│ └── subdir
├── dir2
│ └── report.pdf
└── structure.txt
3 directories, 4 files按照更改时间排序(-t)
[root@blog ~]# tree -t #最新修改的文件排在最后
.
├── anaconda-ks.cfg
├── dir1
│ ├── subdir
│ └── file1.txt
├── dir2
│ └── report.pdf
└── structure.txt
3 directories, 4 files以易读的格式输出文件目录(-h)
[root@blog ~]# tree -h
.
├── [ 1.5K] anaconda-ks.cfg
├── [ 37] dir1
│ ├── [ 0] file1.txt
│ └── [ 6] subdir
├── [ 24] dir2
│ └── [ 0] report.pdf
└── [ 469] structure.txt
3 directories, 4 files生成JSON格式列表(-J)
[root@blog ~]# tree -J
[{"type":"directory","name": ".","contents":[
{"type":"file","name":"anaconda-ks.cfg"},
{"type":"directory","name":"dir1","contents":[
{"type":"file","name":"file1.txt"},
{"type":"directory","name":"subdir","contents":[
]}
]},
{"type":"directory","name":"dir2","contents":[
{"type":"file","name":"report.pdf"}
]},
{"type":"file","name":"structure.txt"}
]},
{"type":"report","directories":3,"files":4}
]3.进阶应用场景
磁盘空间分析
[root@blog ~]# tree --du -h #显示目录磁盘使用情况
.
├── [ 1.5K] anaconda-ks.cfg
├── [ 43] dir1
│ ├── [ 0] file1.txt
│ └── [ 6] subdir
├── [ 24] dir2
│ └── [ 0] report.pdf
└── [ 469] structure.txt
6.0K used in 3 directories, 4 files结合grep过滤内容
[root@blog ~]# tree -f /root | grep txt #筛选含txt的路径
│ ├── /root/dir1/file1.txt
└── /root/structure.txt快速定位大文件
[root@blog ~]# tree -if /boot | grep -E '.*\.[a-zA-Z0-9]{3,}$' | xargs du -h | sort -rh | head -n 10 #使用正则过滤扩展名至少3字符的文件
183M /boot/initramfs-0-rescue-c7b614f13cae4850bfc895f5f2c2917a.img
59M /boot/initramfs-5.14.0-570.12.1.el9_6.x86_64.img
2.5M /boot/efi/EFI/redhat/grubx64.efi
2.3M /boot/grub2/fonts/unicode.pf2
940K /boot/efi/EFI/redhat/shimx64-redhat.efi
940K /boot/efi/EFI/redhat/shimx64.efi
940K /boot/efi/EFI/redhat/shim.efi
940K /boot/efi/EFI/BOOT/BOOTX64.EFI
840K /boot/efi/EFI/redhat/mmx64.efi
92K /boot/efi/EFI/BOOT/fbx64.efi生成网站目录结构图
[root@blog ~]# tree -H /root -o site_map.html --charset utf-8需要将html下载本地,使用浏览器打开效果如下图
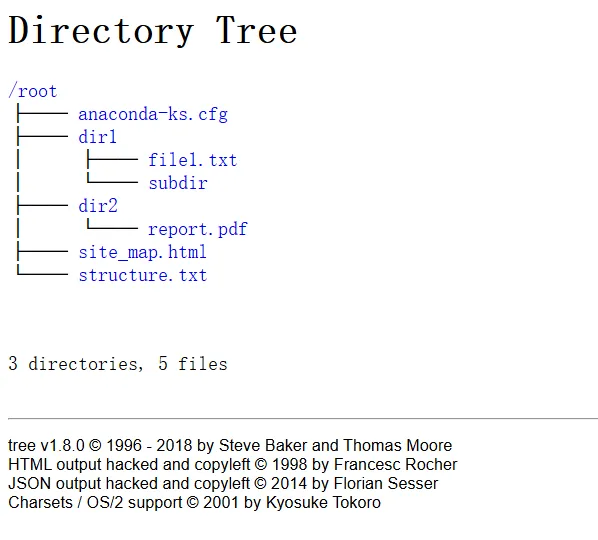
注意事项
善用Tab键补全: 输入路径时,按Tab键可以让系统自动补全目录名或文件名,避免拼写错误并提高效率。
超大目录建议配合-L参数限制遍历层数
在脚本中使用时建议添加--noreport参数禁用统计信息
使用 tree | grep "files"可以显示文件总数,输出末尾会统计
通过man tree查看完整手册


评论区